Money flows clockwise and goods flow counterclockwise.
Equilibrium is the point at which the demand and supply curve meet. If the market price is above this, there is a surplus. If it is below there is a shortage. Eventually the shortage and surplus will decrease and go back to equilibrium.
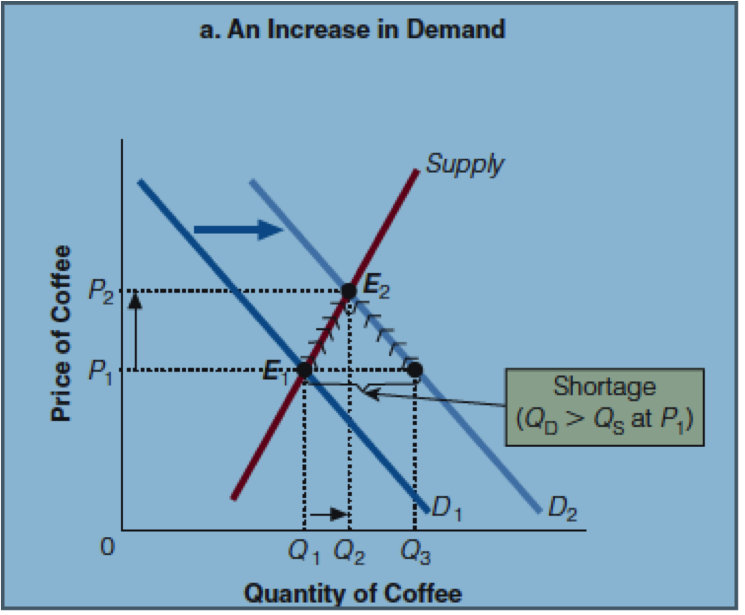
When there is a shortage, consumers bid the price up to comet for goods until the price goes back to equilibrium.
An increase of demand causes a shortage until equilibrium is reached at a higher price and quantity.
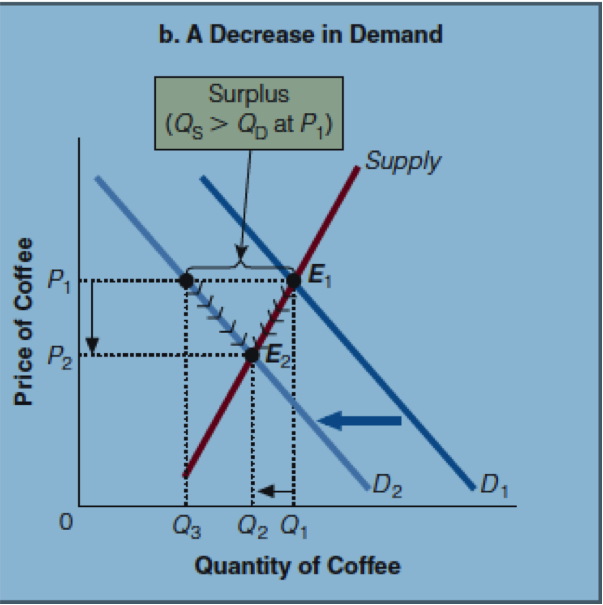
When there is a decrease in demand, there is a surplus. The excess goods decrease the price until a new equilibrium is reached.
A shift in supply and and demand causes a change in the quantity and price. One is always the indeterminate.
Price ceiling:
 A price ceiling sets the maximum price that can be charged for a good, like rent control. This causes a permanent shortage. When the price ceiling is above equilibrium, the price is NOT binding.
A price ceiling sets the maximum price that can be charged for a good, like rent control. This causes a permanent shortage. When the price ceiling is above equilibrium, the price is NOT binding.
Price Floor:
 A price floor is the minimum amount that can be paid for a good, like wages (minimum wage). This concerns the factor market. When the price floor is under equilibrium the price is NOT binding. This causes a surplus of unemployment (low-skilled workers).
A price floor is the minimum amount that can be paid for a good, like wages (minimum wage). This concerns the factor market. When the price floor is under equilibrium the price is NOT binding. This causes a surplus of unemployment (low-skilled workers).
All pictures were taken from a class powerpoint by Professor Robert Sexton, Pepperdine University. The photos can also be found in his economics textbook.